Which Benign Condition Shows Silver Scaly Plaques On The Skin?
An extensive language has been developed to standardize the clarification of skin lesions, including
Rash is a full general term for a temporary skin eruption.
Cantankerous-section of the pare and peel structures
Macules are flat, nonpalpable lesions unremarkably < 10 mm in diameter. Macules correspond a change in color and are not raised or depressed compared to the peel surface. A patch is a large macule. Examples include freckles, flat moles, tattoos, and port-vino stains Capillary Malformations Capillary malformations are present at birth and appear as flat, pink, red, or purplish lesions. Port-wine stains are capillary vascular malformations that are present at birth and that manifest... read more 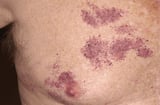 , and the rashes of rickettsial infections Overview of Rickettsial and Related Infections Rickettsial diseases (rickettsioses) and related diseases (anaplasmosis, ehrlichiosis, Q fever, scrub typhus) are acquired by a grouping of gram-negative, obligately intracellular coccobacilli. All... read more
, and the rashes of rickettsial infections Overview of Rickettsial and Related Infections Rickettsial diseases (rickettsioses) and related diseases (anaplasmosis, ehrlichiosis, Q fever, scrub typhus) are acquired by a grouping of gram-negative, obligately intracellular coccobacilli. All... read more 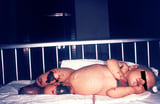 , rubella Rubella (Run into besides Congenital Rubella.) Rubella is a contagious viral infection that may cause adenopathy, rash, and sometimes ramble symptoms, which are commonly mild and brief. Infection during... read more
, rubella Rubella (Run into besides Congenital Rubella.) Rubella is a contagious viral infection that may cause adenopathy, rash, and sometimes ramble symptoms, which are commonly mild and brief. Infection during... read more  , measles Measles Measles is a highly contagious viral infection that is most common amidst children. It is characterized by fever, coughing, coryza, conjunctivitis, an enanthem (Koplik spots) on the oral mucosa... read more than
, measles Measles Measles is a highly contagious viral infection that is most common amidst children. It is characterized by fever, coughing, coryza, conjunctivitis, an enanthem (Koplik spots) on the oral mucosa... read more than  (tin also have papules and plaques), and some allergic drug eruptions Drug Eruptions and Reactions Drugs can crusade multiple skin eruptions and reactions. The virtually serious of these are discussed elsewhere in THE MANUAL and include Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis, hypersensitivity... read more
(tin also have papules and plaques), and some allergic drug eruptions Drug Eruptions and Reactions Drugs can crusade multiple skin eruptions and reactions. The virtually serious of these are discussed elsewhere in THE MANUAL and include Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis, hypersensitivity... read more 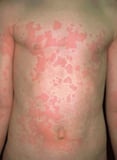 .
.
Papules are elevated lesions usually < 10 mm in diameter that tin can exist felt or palpated. Examples include nevi, warts, lichen planus Lichen Planus Lichen planus is a recurrent, pruritic, inflammatory eruption characterized past minor, discrete, polygonal, flat-topped, violaceous papules that may coagulate into rough scaly plaques, often accompanied... read more 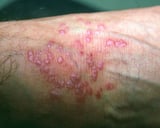 , insect bites, seborrheic keratoses Seborrheic Keratoses Seborrheic keratoses are superficial, oft pigmented, epithelial lesions that are commonly warty just may occur as smooth papules. The cause of seborrheic keratosis is unknown, but genetic mutations... read more
, insect bites, seborrheic keratoses Seborrheic Keratoses Seborrheic keratoses are superficial, oft pigmented, epithelial lesions that are commonly warty just may occur as smooth papules. The cause of seborrheic keratosis is unknown, but genetic mutations... read more 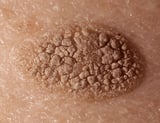 , actinic keratoses Actinic keratoses Chronic affects of sunlight include photoaging, actinic keratoses, and skin cancer. (Run into likewise Overview of Effects of Sunlight.) Chronic exposure to sunlight ages the skin (photoaging, dermatoheliosis... read more
, actinic keratoses Actinic keratoses Chronic affects of sunlight include photoaging, actinic keratoses, and skin cancer. (Run into likewise Overview of Effects of Sunlight.) Chronic exposure to sunlight ages the skin (photoaging, dermatoheliosis... read more  , some lesions of acne Acne Vulgaris Acne vulgaris is the germination of comedones, papules, pustules, nodules, and/or cysts as a effect of obstruction and inflammation of pilosebaceous units (hair follicles and their accompanying... read more
, some lesions of acne Acne Vulgaris Acne vulgaris is the germination of comedones, papules, pustules, nodules, and/or cysts as a effect of obstruction and inflammation of pilosebaceous units (hair follicles and their accompanying... read more  , and skin cancers Overview of Skin Cancer Skin cancer is the most common type of cancer and commonly develops in sunday-exposed areas of pare. The incidence is highest among outdoor workers, sportsmen, and sunbathers and is inversely related... read more . The term maculopapular is oft loosely and improperly used to draw many red rashes; because this term is nonspecific and easily misused, it should be avoided.
, and skin cancers Overview of Skin Cancer Skin cancer is the most common type of cancer and commonly develops in sunday-exposed areas of pare. The incidence is highest among outdoor workers, sportsmen, and sunbathers and is inversely related... read more . The term maculopapular is oft loosely and improperly used to draw many red rashes; because this term is nonspecific and easily misused, it should be avoided.
Urticaria Urticaria Urticaria consists of migratory, well-confining, erythematous, pruritic plaques on the skin. Urticaria also may be accompanied by angioedema, which results from mast cell and basophil activation... read more  (wheals or hives) is characterized by elevated lesions caused by localized edema. Wheals are pruritic and red. Wheals are a common manifestation of hypersensitivity to drugs, stings or bites, autoimmunity, and, less usually, physical stimuli including temperature, pressure, and sunlight. The typical wheal lasts < 24 hours.
(wheals or hives) is characterized by elevated lesions caused by localized edema. Wheals are pruritic and red. Wheals are a common manifestation of hypersensitivity to drugs, stings or bites, autoimmunity, and, less usually, physical stimuli including temperature, pressure, and sunlight. The typical wheal lasts < 24 hours.
Scale is heaped-up accumulations of horny epithelium that occur in disorders such as psoriasis Psoriasis Psoriasis is an inflammatory disease that manifests most ordinarily as well-circumscribed, erythematous papules and plaques covered with silvery scales. Multiple factors contribute, including... read more 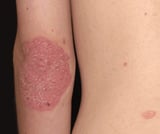 , seborrheic dermatitis Seborrheic Dermatitis Seborrheic dermatitis is a common inflammatory status of skin regions with a high density of sebaceous glands (eg, face, scalp, sternum). The cause is unknown, just species of Malassezia... read more
, seborrheic dermatitis Seborrheic Dermatitis Seborrheic dermatitis is a common inflammatory status of skin regions with a high density of sebaceous glands (eg, face, scalp, sternum). The cause is unknown, just species of Malassezia... read more 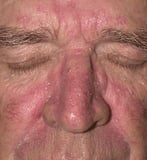 , and fungal infections. Pityriasis rosea Pityriasis Rosea Pityriasis rosea is a self-limited, inflammatory disease characterized by diffuse, scaling papules or plaques. Treatment is normally unnecessary. Pityriasis rosea most commonly occurs between... read more
, and fungal infections. Pityriasis rosea Pityriasis Rosea Pityriasis rosea is a self-limited, inflammatory disease characterized by diffuse, scaling papules or plaques. Treatment is normally unnecessary. Pityriasis rosea most commonly occurs between... read more 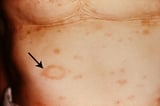 and chronic dermatitis of any type may be scaly.
and chronic dermatitis of any type may be scaly.
Erosions are open areas of pare that result from loss of part or all of the epidermis. Erosions tin can exist traumatic or can occur with various inflammatory or infectious skin diseases. An excoriation is a linear erosion caused by scratching, rubbing, or picking.
Petechiae are nonblanchable punctate foci of hemorrhage. Causes include platelet abnormalities (eg, thrombocytopenia, platelet dysfunction Overview of Platelet Disorders Platelets are cell fragments that function in the clotting system. Thrombopoietin helps control the number of circulating platelets past stimulating the os marrow to produce megakaryocytes,... read more than  ), vasculitis Overview of Vasculitis Vasculitis is inflammation of blood vessels, oft with ischemia, necrosis, and organ inflammation. Vasculitis can touch any blood vessel—arteries, arterioles, veins, venules, or capillaries... read more
), vasculitis Overview of Vasculitis Vasculitis is inflammation of blood vessels, oft with ischemia, necrosis, and organ inflammation. Vasculitis can touch any blood vessel—arteries, arterioles, veins, venules, or capillaries... read more  , and infections (eg, meningococcemia, Rocky Mountain spotted fever Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever (RMSF) Rocky Mount spotted fever (RMSF) is caused by Rickettsia rickettsii and transmitted by ixodid ticks. Symptoms are high fever, severe headache, and rash. (Come across also Overview of Rickettsial... read more than
, and infections (eg, meningococcemia, Rocky Mountain spotted fever Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever (RMSF) Rocky Mount spotted fever (RMSF) is caused by Rickettsia rickettsii and transmitted by ixodid ticks. Symptoms are high fever, severe headache, and rash. (Come across also Overview of Rickettsial... read more than  , other rickettsioses).
, other rickettsioses).
Purpura is a larger expanse of hemorrhage that may be palpable. Palpable purpura is considered the hallmark of leukocytoclastic vasculitis. Purpura may indicate a coagulopathy. Big areas of purpura may exist called ecchymoses or, colloquially, bruises.
Telangiectases are foci of small, permanently dilated blood vessels that may occur in areas of sun harm, rosacea Rosacea Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory disorder characterized by facial flushing, telangiectasias, erythema, papules, pustules, and, in astringent cases, rhinophyma. Diagnosis is based on the characteristic... read more  , systemic diseases (specially systemic sclerosis Systemic Sclerosis Systemic sclerosis is a rare chronic disease of unknown cause characterized by lengthened fibrosis and vascular abnormalities in the peel, joints, and internal organs (especially the esophagus... read more
, systemic diseases (specially systemic sclerosis Systemic Sclerosis Systemic sclerosis is a rare chronic disease of unknown cause characterized by lengthened fibrosis and vascular abnormalities in the peel, joints, and internal organs (especially the esophagus... read more 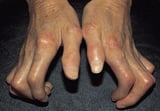 ), or inherited diseases (eg, ataxia-telangiectasia Clutter-Telangiectasia Clutter-telangiectasia results from a DNA repair defect that frequently results in humoral and cellular deficiency; it causes progressive cerebellar ataxia, oculocutaneous telangiectasias, and... read more , hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia is a hereditary disorder of vascular malformation transmitted as an autosomal dominant trait affecting men and women. (See also Overview of Vascular Haemorrhage... read more
), or inherited diseases (eg, ataxia-telangiectasia Clutter-Telangiectasia Clutter-telangiectasia results from a DNA repair defect that frequently results in humoral and cellular deficiency; it causes progressive cerebellar ataxia, oculocutaneous telangiectasias, and... read more , hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia is a hereditary disorder of vascular malformation transmitted as an autosomal dominant trait affecting men and women. (See also Overview of Vascular Haemorrhage... read more 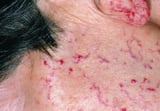 ) or after long-term therapy with topical fluorinated corticosteroids.
) or after long-term therapy with topical fluorinated corticosteroids.
Configuration is the shape of single lesions and the arrangement of clusters of lesions.
Reticulated lesions take a lacy or networked pattern. Examples include cutis marmorata and livedo reticularis.
Some pare lesions accept visible or palpable texture that suggests a diagnosis.
Lichenification is thickening of the skin with accentuation of normal skin markings; it results from repeated scratching or rubbing.
Xanthomas, which are yellowish, waxy lesions, may exist idiopathic or may occur in patients who have lipid disorders.
It is important to annotation whether
-
Lesions are single or multiple.
-
Particular body parts are affected (eg, palms or soles, scalp, mucosal membranes).
-
Distribution is random or patterned, symmetric or asymmetric.
-
Lesions are on lord's day-exposed or protected skin.
Although few patterns are pathognomonic, some are consistent with sure diseases.
Lichen planus Lichen Planus Lichen planus is a recurrent, pruritic, inflammatory eruption characterized by pocket-sized, discrete, polygonal, flat-topped, violaceous papules that may coalesce into rough scaly plaques, often accompanied... read more  oft arises on the wrists, forearms, genitals, and lower legs.
oft arises on the wrists, forearms, genitals, and lower legs.
When examining the color of skin, health care practitioners should note that the natural color of a patient'southward skin can change the appearance of colors.
Cerise skin (erythema) tin can consequence from many different inflammatory or infectious diseases. Cutaneous tumors are often pink or cherry. Superficial vascular lesions such as port-wine stains may appear red.
Orange skin is most often seen in hypercarotenemia, a usually benign condition of carotene degradation after excess dietary ingestion of beta-carotene.
Violet pare may event from cutaneous hemorrhage or vasculitis Overview of Vasculitis Vasculitis is inflammation of blood vessels, often with ischemia, necrosis, and organ inflammation. Vasculitis can affect any blood vessel—arteries, arterioles, veins, venules, or capillaries... read more  . Vascular lesions or tumors, such as Kaposi sarcoma Kaposi Sarcoma Kaposi sarcoma is a multicentric vascular tumor acquired by herpesvirus type eight. It tin occur in classic, AIDS-associated, endemic (in Africa), and iatrogenic (eg, after organ transplantation)... read more
. Vascular lesions or tumors, such as Kaposi sarcoma Kaposi Sarcoma Kaposi sarcoma is a multicentric vascular tumor acquired by herpesvirus type eight. It tin occur in classic, AIDS-associated, endemic (in Africa), and iatrogenic (eg, after organ transplantation)... read more 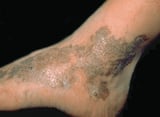 and hemangiomas, tin appear majestic. A lilac color of the eyelids or heliotrope eruption is feature of dermatomyositis Autoimmune Myositis Autoimmune myositis is characterized past inflammatory and degenerative changes in the muscles (polymyositis) or in the pare and muscles (dermatomyositis). Manifestations include symmetric weakness... read more
and hemangiomas, tin appear majestic. A lilac color of the eyelids or heliotrope eruption is feature of dermatomyositis Autoimmune Myositis Autoimmune myositis is characterized past inflammatory and degenerative changes in the muscles (polymyositis) or in the pare and muscles (dermatomyositis). Manifestations include symmetric weakness... read more 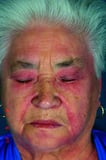 .
.
Shades of blueish, silver, and greyness tin result from deposition of drugs or metals in the skin, including minocycline, amiodarone, and silverish (argyria). Ischemic skin appears purple to gray in color. Deep dermal nevi appear blue.
Blackness skin lesions may exist melanocytic, including nevi and melanoma Melanoma Malignant melanoma arises from melanocytes in a pigmented surface area (eg, pare, mucous membranes, optics, or central nervous arrangement). Metastasis is correlated with depth of dermal invasion. With spread... read more  . Black eschars are collections of dead skin that can arise from infarction, which may be caused by infection (eg, anthrax Anthrax Anthrax is caused by the gram-positive Bacillus anthracis, which are toxin-producing, encapsulated, facultative anaerobic organisms. Anthrax, an frequently fatal disease of animals, is transmitted... read more
. Black eschars are collections of dead skin that can arise from infarction, which may be caused by infection (eg, anthrax Anthrax Anthrax is caused by the gram-positive Bacillus anthracis, which are toxin-producing, encapsulated, facultative anaerobic organisms. Anthrax, an frequently fatal disease of animals, is transmitted... read more 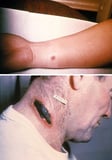 , angioinvasive fungi including Rhizopus, meningococcemia Meningococcal Diseases Meningococci (Neisseria meningitidis) are gram-negative cocci that cause meningitis and meningococcemia. Symptoms, usually astringent, include headache, nausea, vomiting, photophobia, sluggishness... read more than
, angioinvasive fungi including Rhizopus, meningococcemia Meningococcal Diseases Meningococci (Neisseria meningitidis) are gram-negative cocci that cause meningitis and meningococcemia. Symptoms, usually astringent, include headache, nausea, vomiting, photophobia, sluggishness... read more than  ), calciphylaxis Calciphylaxis All patients undergoing long-term renal replacement therapy (RRT) develop accompanying metabolic and other disorders. These disorders crave appropriate attention and adjunctive treatment.... read more
), calciphylaxis Calciphylaxis All patients undergoing long-term renal replacement therapy (RRT) develop accompanying metabolic and other disorders. These disorders crave appropriate attention and adjunctive treatment.... read more  , arterial insufficiency, or vasculitis Cutaneous Vasculitis Cutaneous vasculitis refers to vasculitis affecting small-scale- or medium-sized vessels in the skin and subcutaneous tissue just non the internal organs. Cutaneous vasculitis may be limited to the... read more than
, arterial insufficiency, or vasculitis Cutaneous Vasculitis Cutaneous vasculitis refers to vasculitis affecting small-scale- or medium-sized vessels in the skin and subcutaneous tissue just non the internal organs. Cutaneous vasculitis may be limited to the... read more than  .
.
Dermatographism (dermographism) is the appearance of an urticarial wheal after focal pressure (eg, stroking or scratching the peel) in the distribution of the pressure. Up to 5% of normal patients may exhibit this sign, which is a grade of physical urticaria.
Koebner phenomenon describes the evolution of lesions within areas of trauma (eg, caused by scratching, rubbing, or injury). Psoriasis frequently exhibits this phenomenon, as may lichen planus Lichen Planus Lichen planus is a recurrent, pruritic, inflammatory eruption characterized by small, discrete, polygonal, flat-topped, violaceous papules that may coagulate into crude scaly plaques, ofttimes accompanied... read more  , often resulting in linear lesions.
, often resulting in linear lesions.
Source: https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/dermatologic-disorders/approach-to-the-dermatologic-patient/description-of-skin-lesions
Posted by: smithplagne.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Which Benign Condition Shows Silver Scaly Plaques On The Skin?"
Post a Comment